A Program to find Tokens in C code?
A C program consists of various tokens and a token is either a keyword, an identifier, a constant, a string literal, or a symbol. In C programming, keywords are reserved words that have special meaning and cannot be used for any other purpose. Identifiers are user-defined names for variables, functions, or any other user-defined item. Constants are fixed values that do not change during the execution of a program. String literals are sequences of characters enclosed in double quotes. Symbols are special characters used for various purposes in the program. Each token plays a crucial role in the syntax and semantics of a C program.
Here is a small and simple explanation to find the tokens in a c statement. You can easily check the following C statement consists of five tokens −
printf("Hello, World! \n");
/*
The individual tokens are −
printf (
"Hello, World! \n"
)
;
Semicolons
*/In a C program, the semicolon is a statement terminator. That is, each individual statement must be ended with a semicolon. It indicates the end of one logical entity.
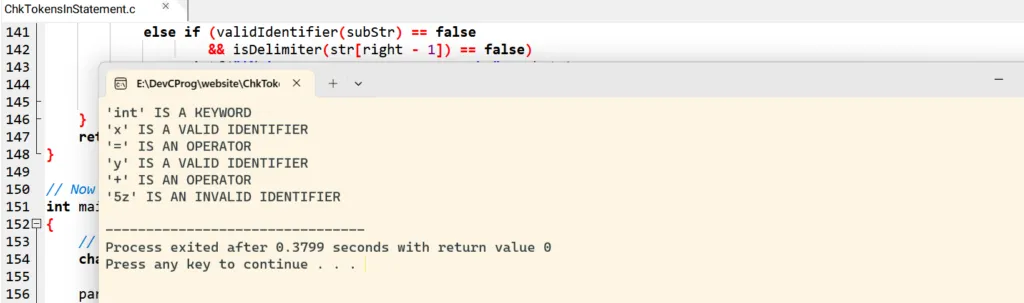
Sample program to check tokens in c statement.
#include